Integration
There are 4 use cases that may lead to integrate switstack moka:
- You need to integrate an EMV Level 3 application on top of
switstack moka. - You need to extend an external entry point with
switstack moka's kernels. - You need to add a new EMV kernel into
switstack mokaframework. - You need to port switstack moka on a new hardware platform.
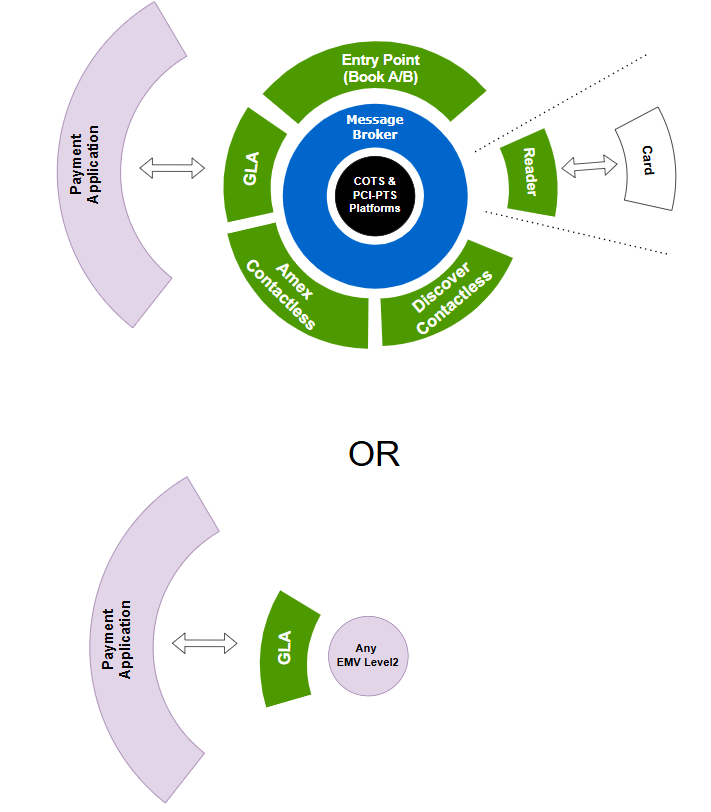
EMV Level 3 integration: GLAse
GLAse stands for Generic Level 2 API service. It is an implementation of GLA, an EMV Level 2 API that is designed to encapsulate any card processing system to manage EMV cards at the Point of Interaction (POI). It is now part of Nexo initiatives consisting in standardizing acceptance software systems. During the past years, different protocols of the merchant ecoystem have been covered by Nexo, including the most famous ones:
- Point Of Sale (POS) through the Nexo Retail protocol.
- Acquirer host through the Nexo Acquirer protocol, a.k.a. ISO 20022.
- Terminal Management System (TMS) through the Nexo TMS protocol.
(See Nexo standards).
Supporting the effort to limit technical dependencies between acceptance system providers and integrators, switstack has recently proposed this API to abstract EMV Level 2. The goal is to:
- Remove dependencies between EMV Level 3 and EMV Level 2 proprietary API.
- Reduce the logical gap between EMV Level 2 certification and EMV Level 2 integration.
- Automate EMV solutions developments.
External entry point integration: switstack moka framework
Compliance with EMVCo Books A/B
switstack moka entry point APIs follow EMVCo Book A/B specifications. Then, a plug-and-play approach is possible.
- Entry point API provides a set of functions enabling granular calls to perform starts A/B/C/D, to set entry point data model, and even control the EMV Level 2 transaction flow.
- There is a simple and minimum coupling between entry point and kernels. Any kernel is activated using an ACT signal (as per Mastercard definition), and the outcomes can be processed in a normalized way.
Info
Activate a kernel using a message broker service abstracting kernel location, or directly call a function.
// Using a message broker call
moka_message_t req, rsp;
msg_brk_prepare_message(
SERVICE_TYPE_ENTRY_POINT,
kernel, // Kernel identifier
CPA_SERVICE_ACTIVATE,
&req, // Message request
inbound_data,
inbound_length,
&rsp, // Message response
outbound,
(*out_length));
service_error = msg_brk_send(x_emvco_entry_point_message_broker, &req, &rsp);
// Using a function call
mastercard_card_processing(
inbound_data, inbound_length, outbound, outbound_length);
Info
Inbound and outbound data followed EMVCo Book A/B specifications.
| ACT Signal Templates | Descriptions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 0xe2 | EMV configuration | e2 81 9f 9f 01 00 9f 09 02 00 02 9f 15 02 11 22 9f 16 00 9f 1a 02 00 56 9f 1c 00 9f 1d 08 6c ff 00 00 00 00 00 00 9f 1e 08 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 9f 33 00 9f 35 01 22 9f 40 05 00 00 00 00 00 9f 4e 00 9f 7e 00 df 81 1b 01 20 df 81 20 05 00 00 00 00 00 df 81 21 05 00 00 00 00 00 df 81 22 05 00 00 00 00 00 df 81 23 06 00 00 00 01 00 00 df 81 24 06 00 00 00 03 00 00 df 81 25 06 00 00 00 05 00 00 df 81 26 06 00 00 00 00 10 00 df 81 17 01 00 df 81 18 01 60 df 81 19 01 08 df 81 1f 01 08 |
| 0xe4 | FCI (without SW1SW2) | e4 3f 6f 3b 84 07 a0 00 00 00 04 10 10 a5 30 87 01 01 50 0a 4d 61 73 74 65 72 43 61 72 64 5f 2d 06 65 6e 64 65 66 72 9f 11 01 01 9f 38 08 9f 02 06 9f 33 03 9c 01 bf 0c 06 9f 5d 03 00 04 00 90 00 |
| 0xe5 | Transaction Related Data (TRD) | e5 15 9f 02 06 00 00 00 00 15 00 9a 03 23 08 01 |
| -- | Primitive data objects | 96 08 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 df a0 0a 09 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 9f 37 04 8e 6f fe cb where 0xdfa00a = entry point indicators for visa-a-like kernels |
| 0xeb | Kernel Resume Data (KRD) | eb 04 8A 02 30 30 |
Info
To analyze kernel outcome, parse outbound data
| OUT Signals | Descriptions | C-8 Signals | Examples | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0xdf8129 | Outcome parameter set | 0x9f8210 | df 81 29 08 40 10 f0 f0 50 f0 ff 00 | -- |
| 0xff8105 | Data record | 0xbf8102 | ff 81 05 81 a8 9f 02 06 00 00 00 00 15 00 9f 26 08 ac 12 34 56 78 9a bc de 5f 24 03 49 12 31 82 02 19 80 50 0a 4d 61 73 74 65 72 43 61 72 64 5a 08 54 13 33 90 00 00 15 13 5f 34 01 01 9f 36 02 00 02 9f 07 02 ff ff 9f 09 02 00 02 9f 27 01 80 9f 34 03 3f 00 01 84 07 a0 00 00 00 04 10 10 9f 1e 08 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 9f 10 12 01 10 00 00 00 02 00 00 da c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 9f 11 01 01 9f 33 03 00 60 08 9f 1a 02 00 56 9f 35 01 22 95 05 00 00 80 00 01 5f 2a 02 09 78 9a 03 23 08 01 9c 01 00 9f 37 04 de ad be ef | -- |
| 0xff8106 | Discretionary data | 0xbf8103 | ff 81 06 32 9f 42 02 09 78 df 81 15 06 01 00 00 00 00 21 9f 6e 20 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 | -- |
| 0xdf8115 | Error indication | 0x9f8204 | df 81 15 06 01 00 00 00 00 21 | Included in discretionary data |
| 0xdf8116 | User interface request data | 0x9f8205 | df 81 16 0d 21 02 00 00 00 65 6e 64 65 66 72 00 00 | -- |
| 0xe7 | switstack moka additional tags |
-- | e7 21 df a0 09 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 df a0 28 05 04 02 00 00 00 df a0 20 06 00 00 00 03 00 00 | switstack moka proprietary tags |
Note
EMV Level 2 signals are not normalized accross brands. switstack moka uses OUT Signals for Mastercard (kernel 0x02), and C-8 Signals - for other kernels.
Full flexibility
With switstack moka, it is possible to add new EMV kernels to a payment application. switstack moka architecture enables different types of integrations to extend existing entry points running their own kernels. Each integration proviving for and drawbacks depending on constraints and objectives.
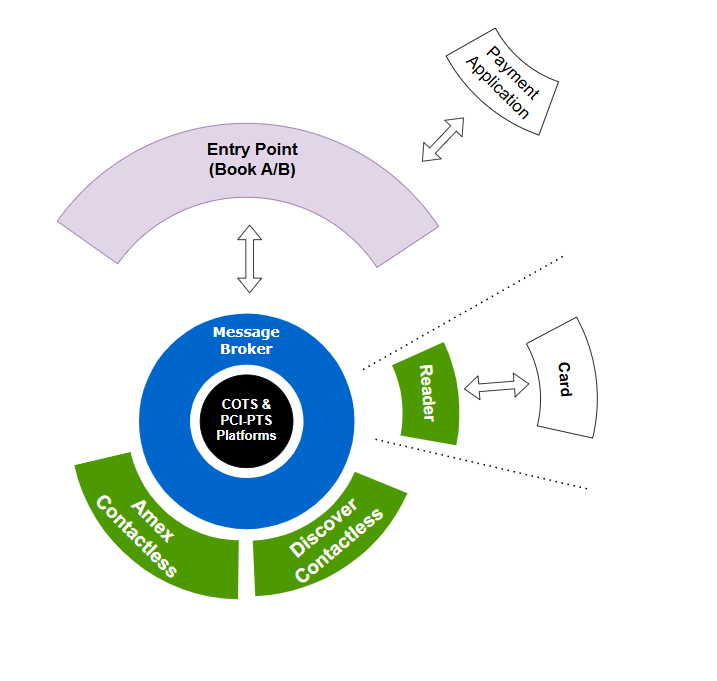
Payment application <-> switstack moka entry point
- You don't want to modify the existing entry point.
- You don't want to break the EMV Level 2 certifications already granted.
- You want to take full advantage of
switstack mokaecosystem, and the test automation framework.
Then:
- Integrate
switstack mokaentry point C API calls into your payment application. - Leverage on an API that provides full control of the card processing to:
- Configure the kernels.
- Trigger the EMV Level 2 flow.
- Process the transactions outcomes.
In that combination, 2 entry points are deployed in "parallel".
| API Functions | Descriptions | Notes | Function Calls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set Parameters | Set entry point data model | See entry_point_generic.h | uint16_t emvco_entry_point_set_parameters(const uint8_t* inbound, uint16_t in_length) |
| Start A | Perform pre-processing | See entry_point_functions.h | uint16_t emvco_entry_point_start_a(const uint8_t inbound, uint16_t in_length, uint8_t outbound, uint16_t* out_length) |
| Start B | Perform protocol activiation | See entry_point_functions.h | uint16_t emvco_entry_point_start_b(uint8_t* detected_interface) |
| Start C | Perform combination selection | See entry_point_functions.h | uint16_t emvco_entry_point_start_c(uint8_t outbound, uint16_t out_length) |
| Start D | Activate kernel | See entry_point_functions.h | uint16_t emvco_entry_point_start_d(uint8_t outbound, uint16_t out_length) |
Note
Inbound and outbound data follow ASN.1 TLV format.
| Tags | Descriptions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0xdfa021 | Signal mode for certification | Use this parameter to define signal format coming out the entry point. Default = Mastercard = 0x00 |
| 0xdfa025 | Reference transaction type | Use this parameter to filter combinations at start A by transaction type. Default = Purchase = 0x00 |
| 0xdfa00b | Starting condition for entry point, a.k.a. autorun | |
| 0xdfa00c | Skip polling at start B time | |
| 0xdfa011 | Support ASPRD tag 0x9F0A | Use this parameter to support Application Selection Registered Proprietary Data |
| 0xdfa013 | Support TIDAS tags 0x9F3E/0x9F3F | Support Terminal Information During Application Selection |
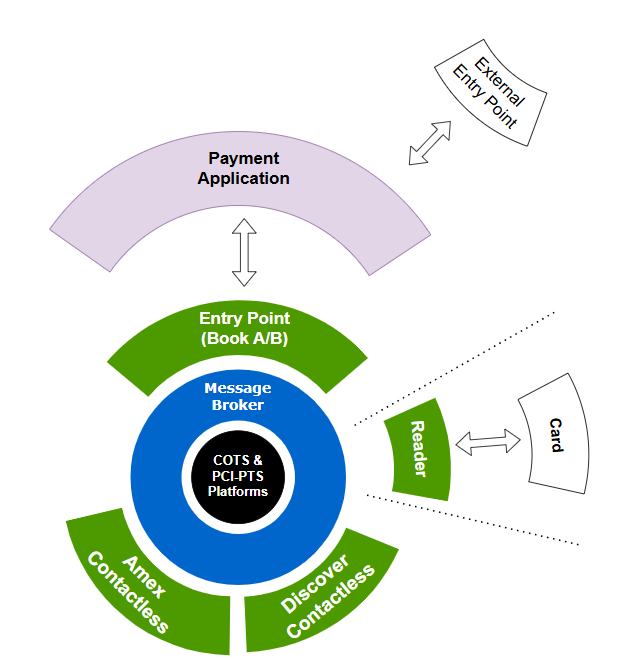
External entry point <-> switstack moka kernels
Hypothesis: the existing entry point runs on the same physical host as switstack moka entry point.
- You need to take control of the entry point, and are ready to modify it.
- You want to take full advantage of
switstack mokaecosystem, and the test automation framework.
Then:
- Integrate directly
switstack moka's kernels withoutswitstack mokaentry point. - Leverage on an API that follows EMVCo Books A/B:
- Activate the kernels
- Process final outcomes.
In that combination, your entry point integrates switstack moka kernels that live in "parallel" with other kernels.
EMV Kernel integration: switstack moka service
[Develop your own kernel into switstack moka framework and use the test automation framework. More details to come in next version]
Hardware integration: switstack moka HAL
Porting moka on a new hardware platform involves:
- Connecting HAL functions to actual platform APIs
- Overloading Display service aiming at presenting messages coming out from moka
- If supported, integrating a pin pad
Porting moka's HAL
In order to "deploy" moka on a new hardware platform, you need to connect a series of moka's APIs to the actual platform's services. Moka's HAL is pretty thin so that task is really straight forward. It requires a good knowledge of the targeted platform, and a good integration test strategy (avoid big bang integration!). HAL functions to be ported are directly related to EMV features that a payment platform needs to support. They are as followed:
| moka's HAP API | Porting | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| hal_crypt_rng.h | Mandatory | True random number generation |
| hal_crypt_sha.h | Optional | moka proposes a software version but a hardware one may be faster |
| hal_crypt_rsa.h | Optional | moka proposes a software version but a hardware one may be faster |
| hal_emv_card.h | Mandatory | All EMV Level 1 related features (PCI-PTS) or NFC based API to communicate with EMV cards: polling, apdu exchanges, antenna management, collision, ... |
| hal_emv_terminal.h | Optional | Terminal PCI-PTS identifier and serial number management |
| hal_emv_platform.h | Optional | Terminal COTS identifier, serial number, version, vendor name, etc... management. Not EMV related |
Other API not listed above leverage on POSIX API. Depending on the new hardware platform, some adaptations may be required. But most of PCI-PTS and COTS platforms are compliant with the moka's vanilla implementation (memcpy, memset, memcmp, strlen, ...).
Overloading Display service
Display is a moka service that implements DISPLAY_SERVICE_UI_REQUEST. Any EMV Level 2 and the entry point need to send a message out during the card processing. All these messages fall down into Display service so it can be easily re-routed anywhere by integrators based on the targeted hardward platform's architecture. For the purpose of moka qualification, that service simply performs a log. The integrator only need to display the message where it is appropriated.
Integrating a pin pad
A pin pad is a critical component that features two APIs (beyond its configuration requirements like keys injection): - Enter PIN - Get PIN block
For EMV contactless, Online PIN is managed as a post-condition of the card processing. Hence, moka doesn't really integrate that capability. It is EMV Level 3's responsibility to detect from the an out signal (Outcome Parameter Set and CVM status generated by moka) whether a PIN entry shall be initiated. Hence, this porting aspect is out of the scope of moka porting.
For contact and offline PIN management, that feature is not supported yet.